Data privacy and security are in a peculiar state in recent years.
We’re currently experiencing an unprecedented level of threats targeting our data, whether that’s vulnerable big data stores or hacking attacks. Yet, in the same breath, cybersecurity practices, regulations, technologies, and general cyber awareness are at their best.
Data privacy, for that matter, is not a uniquely modern-day conundrum. The first “Right to Privacy” was conceived in 1890 by 2 American lawyers, Samuel D. Warren and Louis Brandeis. Perhaps it’s not extreme to suggest humans have been grappling with privacy issues for as long as civilization itself.
Now, in the 21st Century, technology puts the world in our hands and unlimited amounts of information at the end of our fingertips. But what price do we pay to enjoy the benefits of the information age? And are data privacy and security practices doing enough? To help unpack that question a little further, we’ve compiled 100+ data privacy and data security statistics.
We’ll delve into the world of privacy issues, objections, risks, and regulations in this article. But before we get into our assortment of statistics, it’s probably best we take a look at some key definitions first. Data privacy and data security are 2 good places to start…
What is Data Privacy & Data Security?
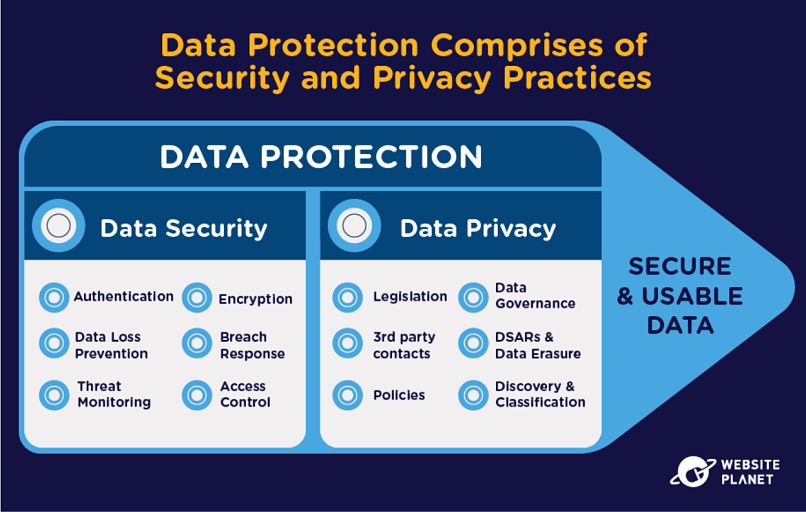
Data privacy, also known as information privacy, is the area of data protection concerned with regulations. In particular, data privacy outlines the ways companies/individuals should properly collect, share, and use sensitive, personal, and/or confidential data (such as financial records or intellectual properties) in line with the law.
Data security is more about the practice of protecting data. If data privacy is “what” you should/shouldn’t do with data, data security is “how” you’re going to make sure data is protected.
Data security covers every way data handlers can avoid the unauthorized access, theft, or corruption of digital information from bad actors. This includes a range of practices, from the physical security of hardware and storage devices to the authentication controls on servers, networks, and devices.
Data security also includes each organization’s policies and procedures. If done correctly, proper data security strategies prevent data compromise and attempts to steal data from cybercriminals.
When we talk about these terms together, then, we are talking about the general state of data protection — both with regards to the legislation that protects our data and the companies or individuals that handle it.
General Stats
As you probably already know, everyone wants your data. Companies want it, governments want it, and (worst of all) criminals want it. Knowledge is power, after all.
We’ll begin with a few general statistics on the state of data protection and data collection.
1. We Generate a Lot of Data

Humans are generating vast quantities of data every day.
With so much data available, it makes sense for companies to capitalize. They can use data to improve your customer experience, target you with the right marketing materials, sell your data to make money, or use that data to provide other services.
2. People Want Online Security

Woah! Easy there, tiger… Perhaps there’s no better way to set the mood than with the statement above.
Given how much people love that other thing, they must be pretty unsatisfied with their online security to consider giving it up. This points to the sorry state of online security and the desperation users have to keep their data secure.
3. Data Collection is…
INNOVATION AND DATA PRIVACY ARE NOT NATURAL ENEMIES: INSIGHTS FROM KOREA’S EXPERIENCE
The following is a guest post to the FPF blog authored by Dr. Haksoo Ko, Professor at Seou…














