
Twitter was thrown into chaos on Wednesday after accounts for some of the world’s most recognizable public figures, executives and celebrities starting tweeting out links to bitcoin scams. Twitter says the attack happened because someone tricked or coerced an employee into providing access to internal Twitter administrative tools. This post is an attempt to lay out some of the timeline of the attack, and point to clues about who may have been behind it.
The first public signs of the intrusion came around 3 PM EDT, when the Twitter account for the cryptocurrency exchange Binance tweeted a message saying it had partnered with “CryptoForHealth” to give back 5000 bitcoin to the community, with a link where people could donate or send money.
Minutes after that, similar tweets went out from the accounts of other cryptocurrency exchanges, and from the Twitter accounts for democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden, Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, President Barack Obama, Tesla CEO Elon Musk, former New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg and investment mogul Warren Buffett.
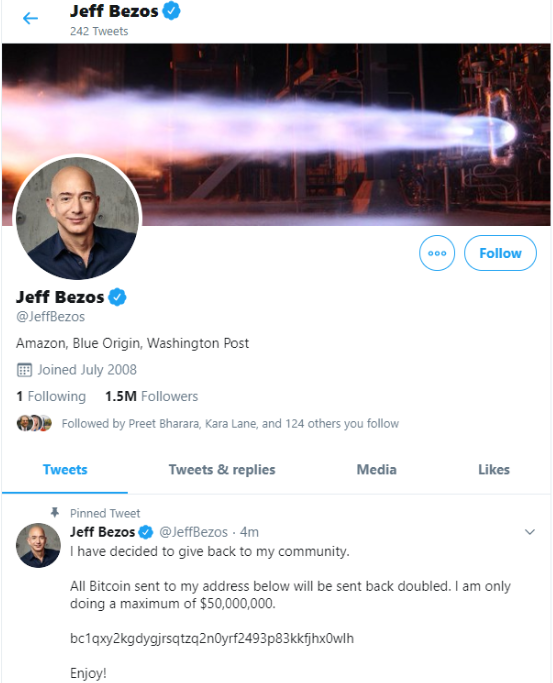
While it may sound ridiculous that anyone would be fooled into sending bitcoin in response to these tweets, an analysis of the BTC wallet promoted by many of the hacked Twitter profiles shows that over the past 24 hours the account has processed 383 transactions and received almost 13 bitcoin — or approximately USD $117,000.
Twitter issued a statement saying it detected “a coordinated social engineering attack by people who successfully targeted some of our employees with access to internal systems and tools. We know they used this access to take control of many highly-visible (including verified) accounts and Tweet on their behalf. We’re looking into what other malicious activity they may have conducted or information they may have accessed and will share more here as we have it.”
There are strong indications that this attack was perpetrated by individuals who’ve traditionally specialized in hijacking social media accounts via “SIM swapping,” an increasingly rampant form of crime that involves bribing, hacking or coercing employees at mobile phone and social media companies into providing access to a target’s account.
People within the SIM swapping community are obsessed with hijacking so-called “OG” social media accounts. Short for “original gangster,” OG accounts typically are those with short profile names (such as @B or @joe). Possession of these OG accounts confers a measure of status and perceived influence and wealth in SIM swapping circles, as such accounts can often fetch thousands of dollars when resold in the underground.
In the days leading up to Wednesday’s attack on Twitter, there were signs that some actors in the SIM swapping community were selling the ability to change an email address tied to any Twitter account. In a post on OGusers — a forum dedicated to account hijacking — a user named “Chaewon” advertised they could change email address tied to any Twitter account for $250, and provide direct access to accounts for between $2,000 and $3,000 apiece.
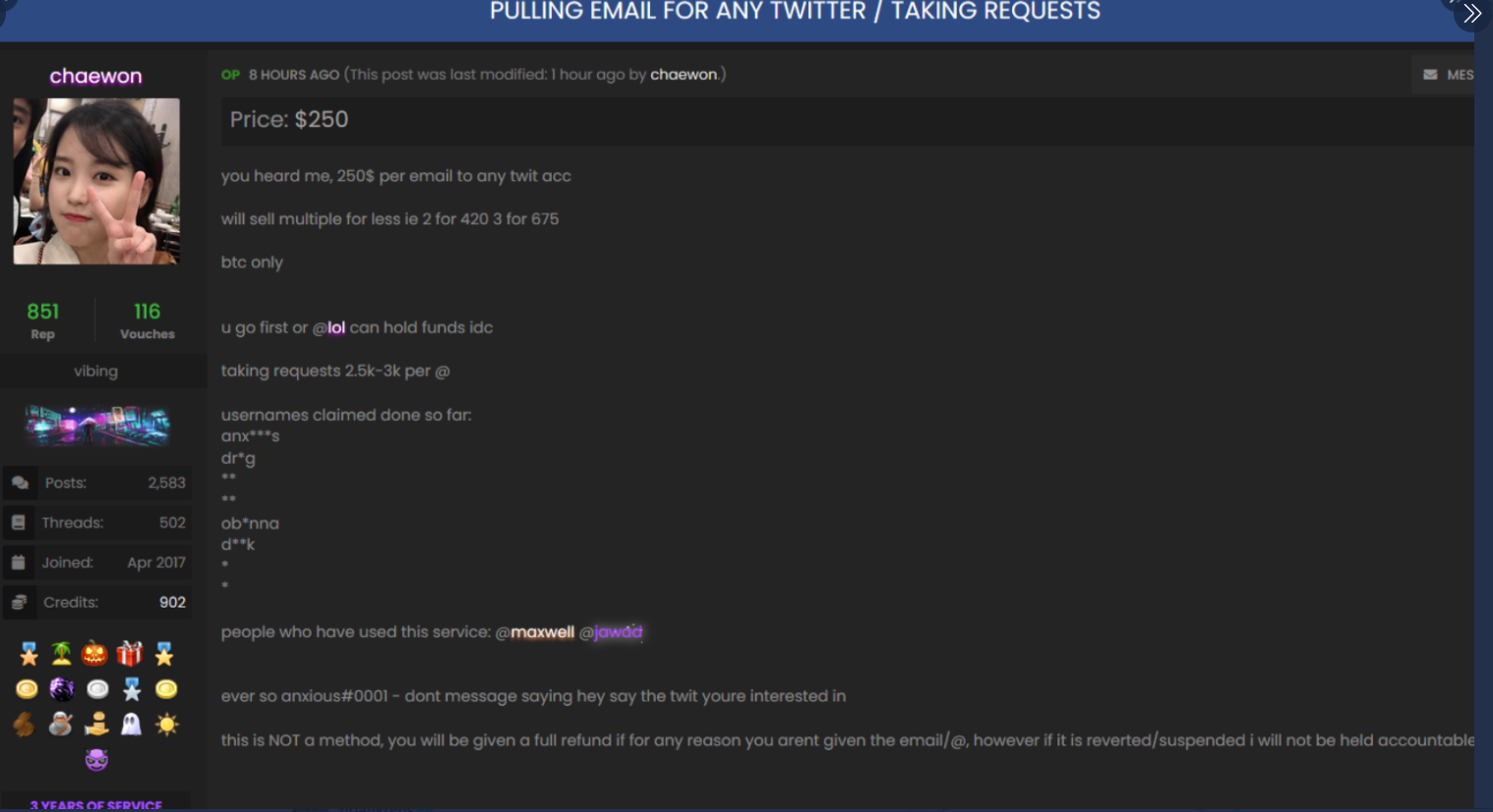
The OGUsers forum user “Chaewon” taking requests to modify the email address tied to any twitter account.
“This is NOT a method, you will be given a full refund if for any reason you aren’t given the email/@, however if it is revered/suspended I will not be held accountable,” Chaewon wrote in their sales thread, which was titled “Pulling email for any Twitter/Taking Requests.”
Hours before any of the Twitter accounts for cryptocurrency platforms or public figures began blasting out bitcoin scams on Wednesday, the attackers appear to have focused their attention on hijacking a handful of OG accounts, including “@6.”
That Twitter account was formerly owned by Adrian Lamo — the now-deceased “homeless hacker” perhaps best known for breaking into the New York Times’s network and for reporting Chelsea Manning‘s theft of classified documents. @6 is now controlled by Lamo’s longtime friend, a security researcher and phone phreaker who asked to be identified in this story only by his Twitter nickname, “Lucky225.”
Lucky225 said that just before 2 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, he received a password reset confirmation code via Google Voice for the @6 Twitter account. Lucky said he’d previously disabled SMS notifications as a means of receiving multi-factor codes from Twitter, opting instead to have one-time codes generated by a mobile authentication app.
But because the attackers were able to change the email address tied to the @6 account and disable multi-factor authentication, the one-time authentication code was sent to both his Google Voice account and to the new email address added by the attackers.
“The way the attack worked was that within Twitter’s admin tools, apparently you can update the email address of any Twitter user, and it does this without sending any kind of notification to the user,” Lucky told KrebsOnSecurity. “So [the attackers] could avoid detection by updating the email address on the account first, and then turning off 2FA.”
Lucky said he hasn’t been able to review whether any tweets were sent from his account during the time it was hijacked because he still doesn’t have access to it (he has put together a breakdown of the entire episode at this Medium post).
But around the same time…
Ontario’s New Privacy Impact Assessment Requirements: What You Need to Know
November 2025, A Major Shift in Privacy Compliance If your organization is a provincial go…















